10 minutes maximum! Can you do it in 5? |
||||||||||||||||||
| 1-4. These questions are about Rutherford scattering as observed in Geiger and Marsden's experiment. | ||||||||||||||||||
1. What was the particle and target material in this experiment?
| ||||||||||||||||||
2. Rutherford estimated the size of the nucleus using 'closest approach' calculations. At the point of closest approach, which of these statements is true?
|
||||||||||||||||||
3. Rutherford predicted that, for particles with the same initial energy, the relative intensity of scattered particles would decrease as the scattering angle increased as shown here.
However at high energies, the scattering pattern deviated from Rutherford's predictions. Which of the following graphs best shows this deviation? |
||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
4. The deviation from the expected pattern provides evidence for...
| ||||||||||||||||||
5. A helium nucleus consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons. Which of the following will have a radius of approximately double that of a helium nucleus?
|
||||||||||||||||||
6. The calculation in question 5 relies on the fact that ...
|
||||||||||||||||||
Q7-8. This diagram shows electron energy levels in a hydrogen atom. Only the first 4 energy levels are shown. Emission or absorption of a photon is associated with an electron jump between energy levels.
|
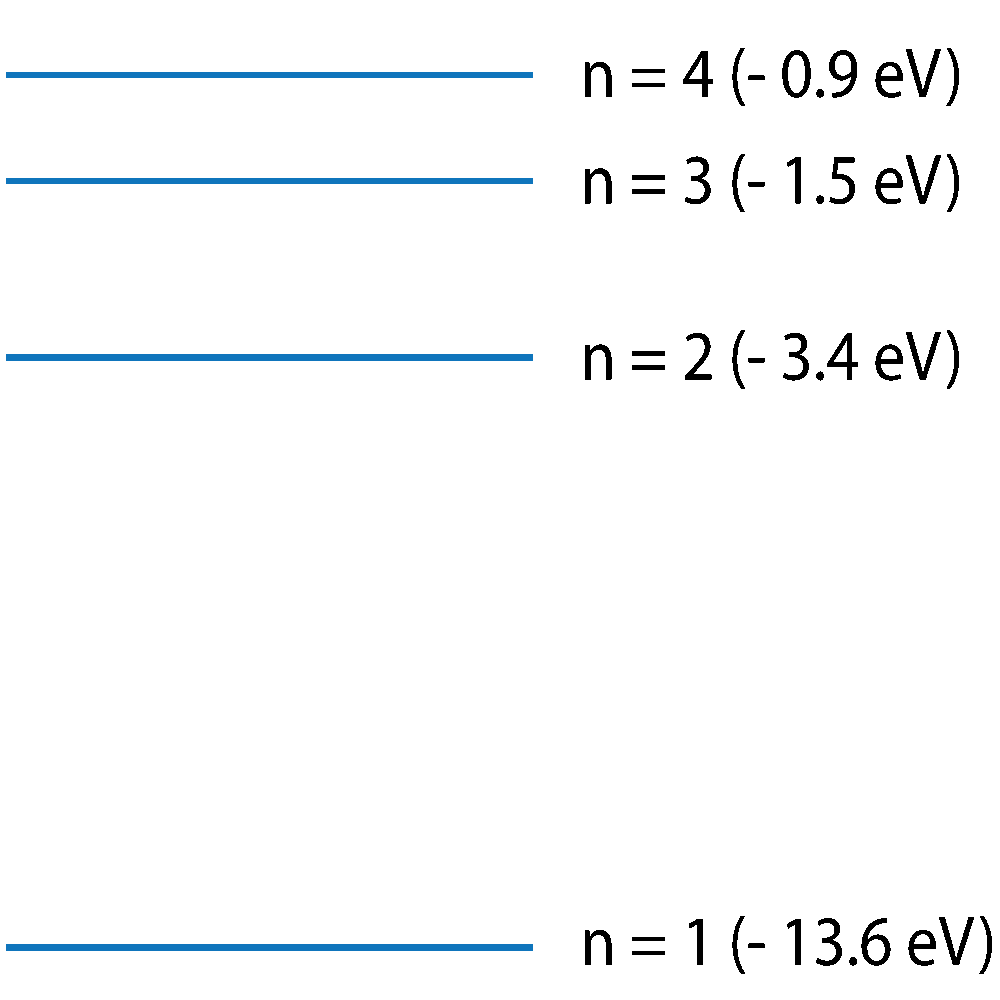
(Not to scale -approximate energy level values). |
|||||||||||||||||
7. Which of the following can be used to calculate the value of the energy released when an electron drops from n=3 to n=1?
| ||||||||||||||||||
8. A transition from n=4 to n=2 emits a photon of blue light of wavelength close to 500nm. Which of the following transitions would emit visible red light, of approximately 650 nm wavelength?
|
||||||||||||||||||
9+10. Electron orbits are quantised in the Bohr model of the atom, where $mvr = {{nh} \over {2\pi}}$. 9. What is the quantity mvr in this equation? |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
10. What is the change in mvr when an electron drops from n=4 to n=2?
| ||||||||||||||||||