Q1-5: These questions are about the processes occuring in a typical nuclear fission reactor: |
 |
||||||||||||||||
1.Which of the following answers best describes the process of nuclear fission in a nuclear reactor? |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
2. Which isotope of uranium is the fissile material in the fuel rods in a typical nuclear reactor?
|
|||||||||||||||||
3. Spontaneous fission by random decay happens continuously. However fission can also be induced in uranium by the impact of which particles?
|
|||||||||||||||||
4. The end products of a uranium nucleus fission reaction are 2 or 3 more particles, and 2 daughter nuclei X and Y. The original uranium nucleus will have ...
| |||||||||||||||||
5. In the first stage of a chain reaction, the uranium nuclei is hit by one particle, releasing on average 2.5 more particles. These go on to hit additional uranium nuclei causing more fission to occur. To the nearest particle, how many on average are released after the 4th stage of a fission chain reaction, assuming all particles strike a uranium nucleus? |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
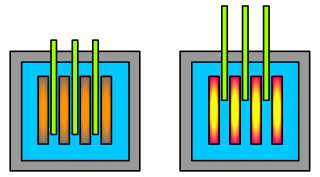
6. This is a diagram of a nuclear reactor. When the top green rods are lifted as shown, the reaction rate increases. What is the name given to these rods and what do they do? |
 |
||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
7. Around the control rods and fuel rods is a moderator material. This is required to...
| |||||||||||||||||
8. Which of the following statements describes the daughter nuclei by-products of a fission reaction?
| |||||||||||||||||
Q9+10: These questions are about calculating the energy released during a fission reaction. Isotope P is hit by a particle X, and splits into isotope Q and R, releasing 2 more X particles in the process. P + X → Q + R + 2X The following data describes these nuclei:
|
|||||||||||||||||
9. Approximately how much energy is released in the above fission reaction for a single nuclei of P?
| |||||||||||||||||
10. Which of the following best describes the changes in mass defect and binding energy after the reaction? |
|||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||