| Speed, Acceleration, Forces, Graphs |
| 1&2. A motorbike moves along a road at 25m/s.
Calculate .. |
 |
1. The distance moved in 50s.
- A). 2 m
- B). 0.5 m
- C). 125 m
- D). 1.25 km
|
|
|
2. The time taken to travel 2 kilometres.
- A). 4 s
- B). 80 s
- C). 0.08 s
- D). 40 s
|
|
3. Which of these is the correct formula for acceleration?
- A). change in velocity x time taken
- B). change in velocity ÷ time taken
- C). velocity x time taken
- D). velocity ÷ time taken
|
|
4. A train accelerates from 10 m/s to 50 m/s in 20 seconds. The acceleration is:
- A). 2 m/s2
- B). 2.5 m/s2
- C). 800 m/s2
- D). 1000 m/s2
|
|
5+6. In a formula 1 car race the acceleration of the first few cars was measured from the start grid.
What are the missing values?
|
Starting velocity (m/s) |
Final velocity (m/s) |
Time taken (s) |
acceleration (m/s2) |
| 5. |
5 |
30 |
|
5 |
| 6. |
0 |
|
12 |
6 |
|
7. If a car accelerates at - 3 m/s2, what does this mean?
- A). It is moving backwards at a constant speed
- B). It is slowing down
- C). It is accelerating but 3 m/s2 less than before
- D). It is accelerating, but the resultant force is backwards
|
|
8. Which of these 4 distance (s) -time (t) graphs shows a car accelerating?
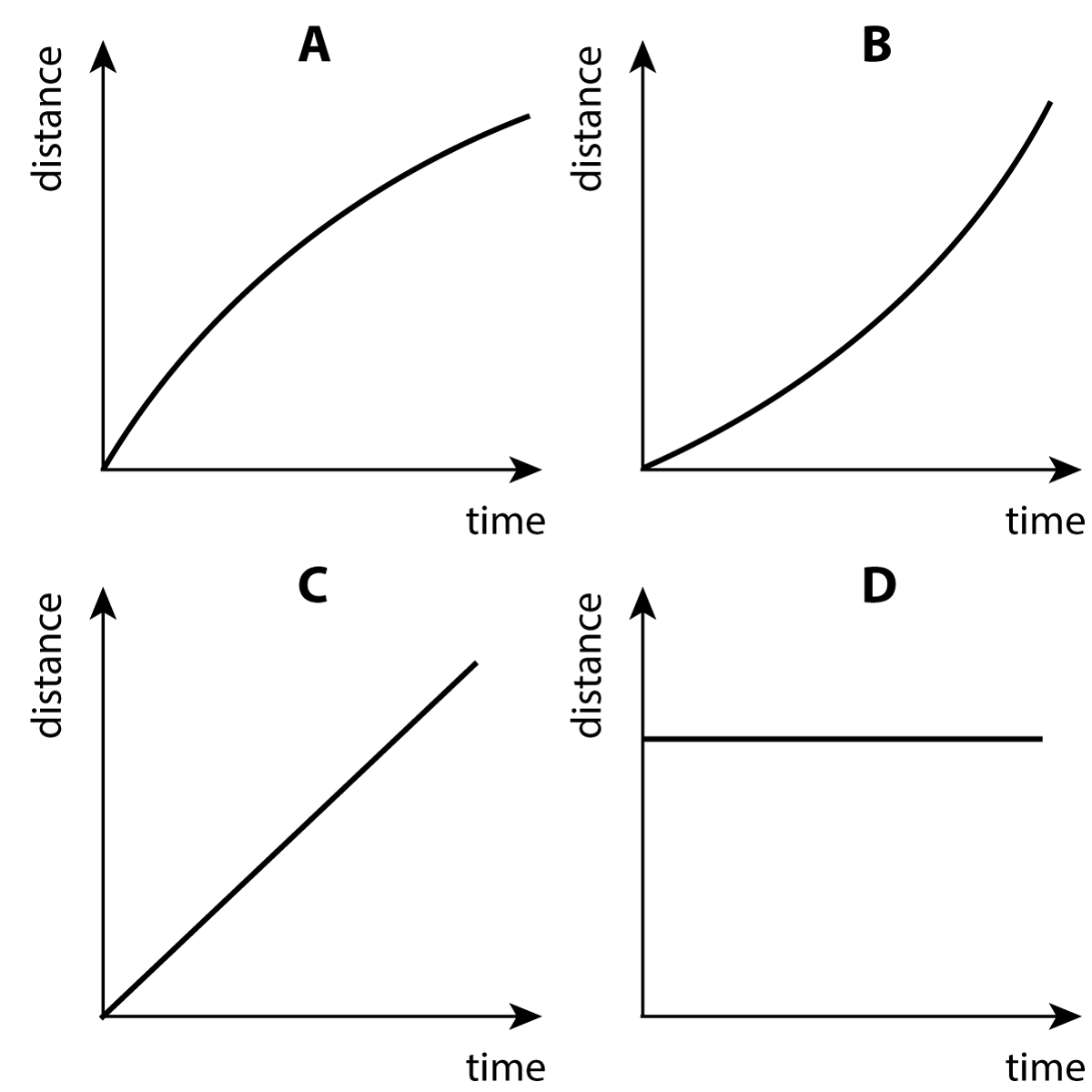
|
|
9-12: This velocity-time graph shows the journey of a bus as it moves away from a road junction.
What quantity is shown by... |
|
| 9. The gradient of line A? |
|
| 10. Line B? |
|
| 11. The area under the line? |
|
| 12. The gradient of line C? |
|
|



