Diffraction, Refraction, Interference, Intensity, Polarisation, Standing Waves |
||
1. The effects of diffraction are clearest in a demonstration when two quantities are similar. What are these quantities?
|
||
2. Which of the following diagrams best shows light wavefronts passing from air, left to right through a block of glass? (Not all wavefronts are shown).
|
||
3. A light ray passes from water into glass. The velocity of light in water is 2.30 x 108 ms-1 and in the glass is 2.00 x 108 ms-1. What is the refractive index of the water / glass boundary?
|
||
4. A light ray is incident on a glass block as shown. The refractive index of the glass/air boundary is 1.5 and the value of sin(300) is 0.5 . |
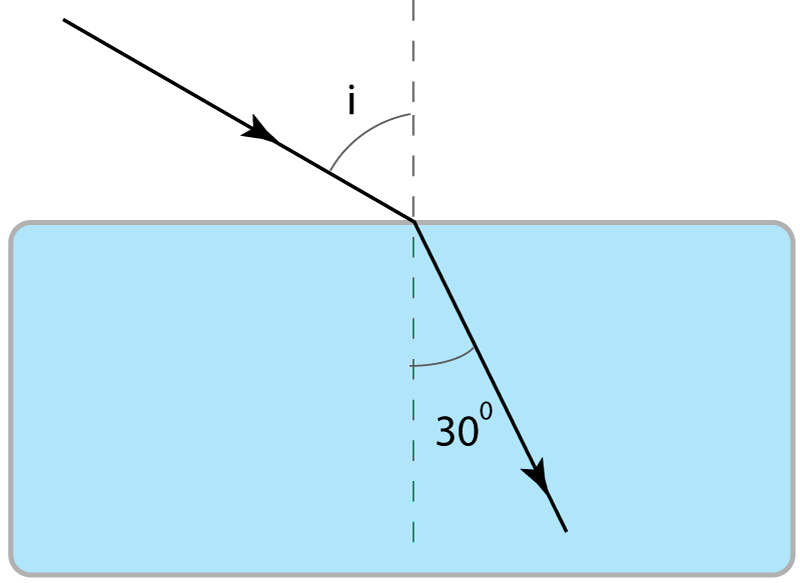 |
|
What is the value of sin (i)?
|
||
5. Total internal reflection can occur when light is trapped inside any transparent substance. This is used in optical fibres.
|
||
To ensure total internal reflection occurs and the light ray remains inside the substance ...
|
||
6. The intensity I of sound waves is measured at a distance x away from a loud speaker. The amplitude of the sound waves measured is A. If the amplitude is increased to 4A and then the distance increased to 2x, the measured intensity will be ...
|
||
7-10: A red laser is directed at two narrow slits as shown in the diagram below. Diffraction occurs, and the two rays P and Q arrive at a point on the screen.
|
||
7. Destructive interference between the 2 rays will occur if ...
|
||
8. The adding together of two waves like this is correctly termed the ...
|
||
9. Two waves will produce constructive interference if the phase difference is ...
|
||
10. An interference pattern will only occur between any two waves if ...
|
||