|
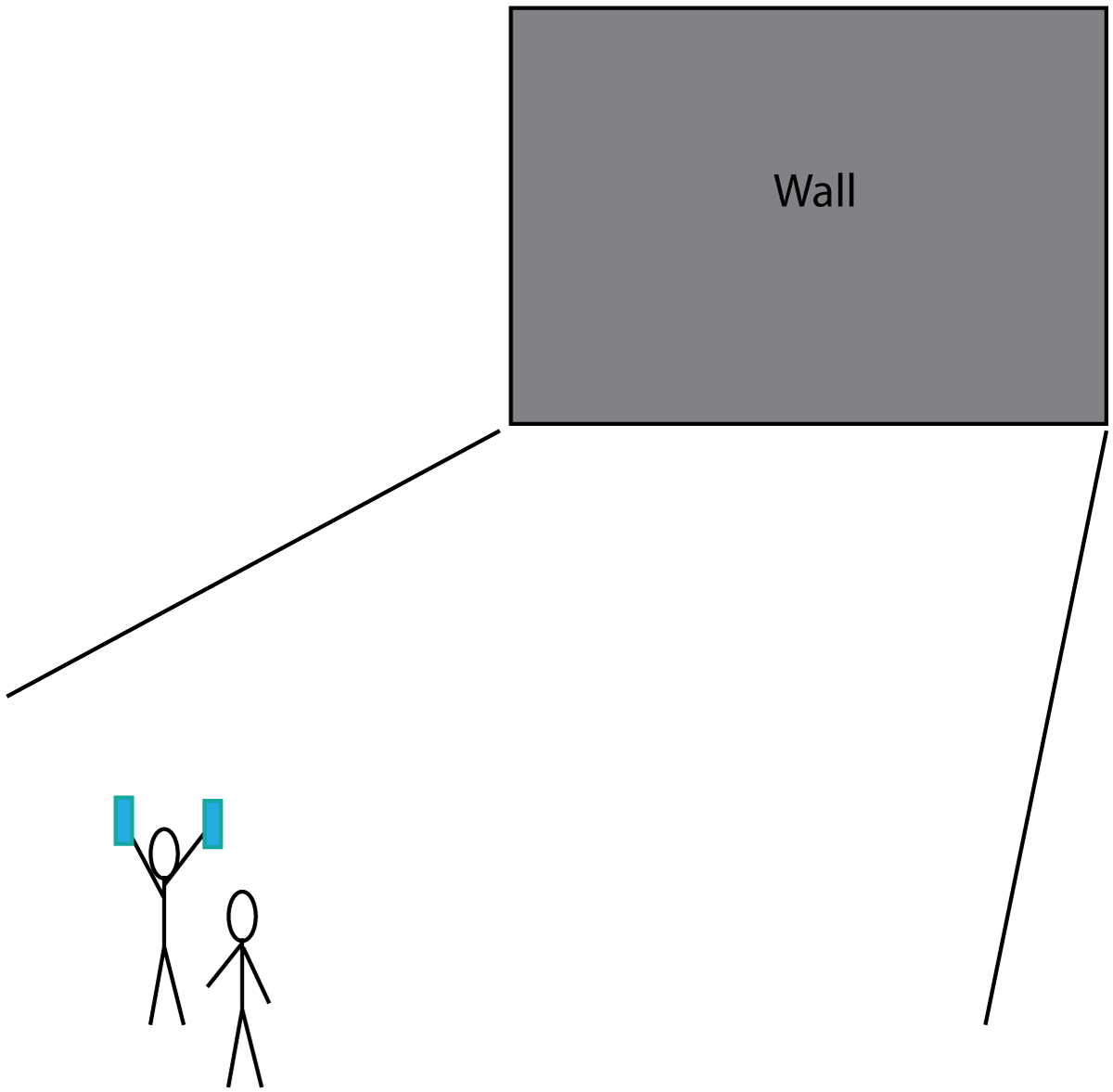
16+17: A sound wave is produced by a student banging two wooden blocks together. The student is 50m from a large wall. After 0.3s an echo is heard. |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
16. What causes the echo?
|
||||||||||||||||||
17. What is the speed of the sound wave produced?
|
||||||||||||||||||
18-20: What are the missing values in this table showing data for sound waves travelling through different substances? |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
21. If light his the inside surface of a glass block at a large angle of incidence, it is reflected. The smallest angle at which this occurs is called the ...
|
||||||||||||||||||
22. What is the name of this effect?
|
||||||||||||||||||
23. Which one of these devices makes use of this effect?
|
||||||||||||||||||
24. Which of these gives the range of human hearing?
|
||||||||||||||||||
25 -27: The diagram below shows 4 sound waves displayed on an oscilloscope screen.
Which of these diagrams shows... |
||||||||||||||||||
| 25. A loud, high pitched sound? | ||||||||||||||||||
| 26. A quiet, high frequency sound? | ||||||||||||||||||
| 27. A high volume, short wavelength sound? | ||||||||||||||||||
28. Which of these lines correctly shows the path of a ray of light through a block of glass?
|
||||||||||||||||||
29. The black line in this diagram shows how light is refracted by a a glass block. If a tank full of water was used instead, which red line would show the direction of the new ray?
|
||||||||||||||||||
| 30. The diagram shows how a lens bends light. Which type of lens is it, and what is point x called? | 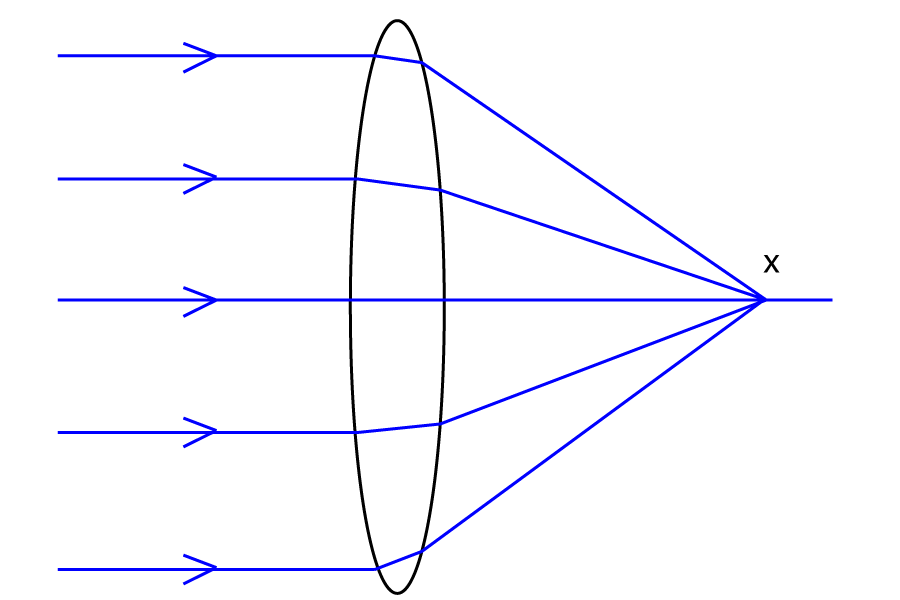 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||